Lead-acid Batteries & Lithium Batteries
1. Lead-acid Batteries
1.1 What is Lead-acid Batteries?
● Lead-acid battery is a storage battery whose electrodes are mainly made of lead and its oxides, and whose electrolyte is sulfuric acid solution.
● The nominal voltage of a single-cell lead-acid battery is 2.0V, which can be discharged to 1.5V and charged to 2.4V.
● In applications, 6 single-cell lead-acid batteries are often connected in series to form a nominal 12V lead-acid battery.
1.2 Lead-acid Battery Structure
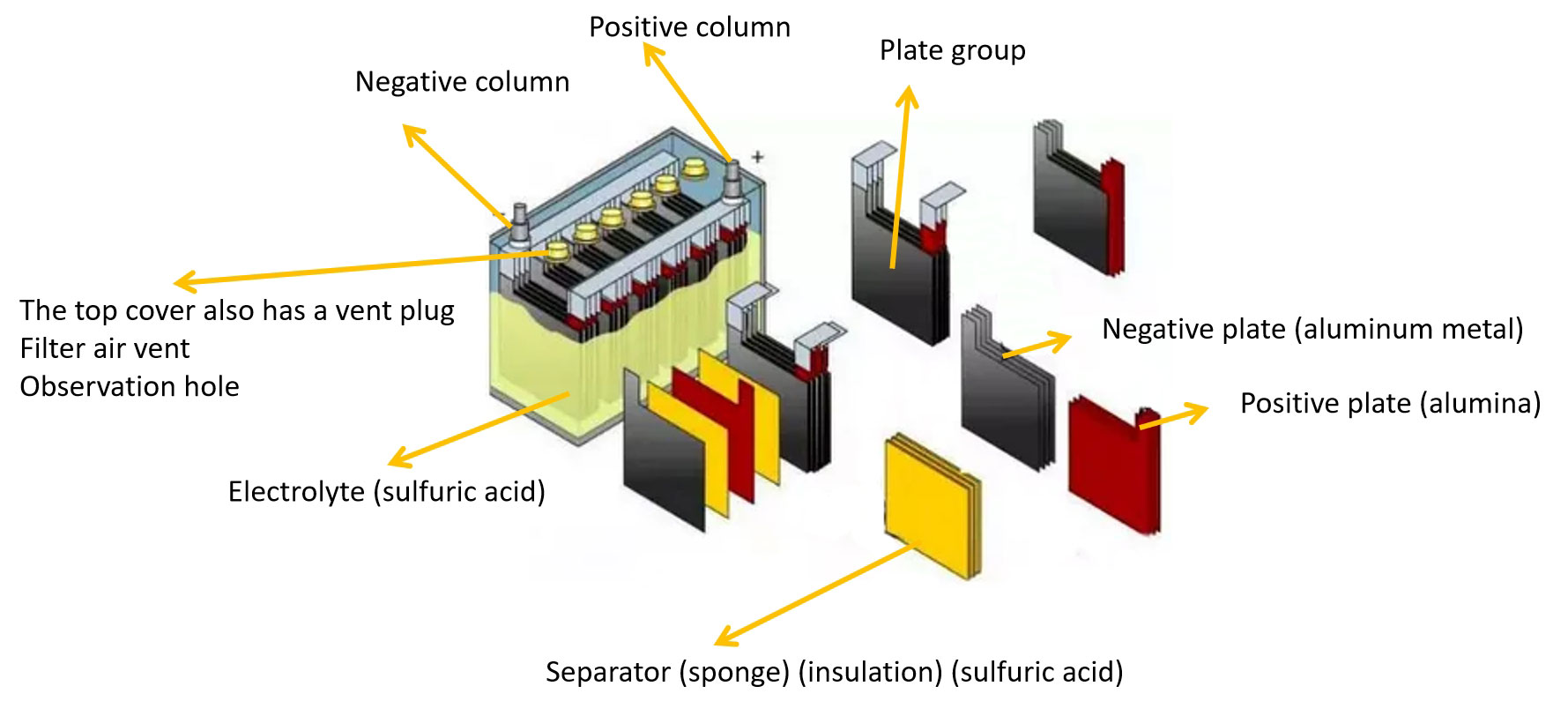
● In the discharge state of lead-acid batteries, the main component of the positive electrode is lead dioxide, and the current flows from the positive electrode to the negative electrode, and the main component of the negative electrode is lead.
● In the charge state of lead-acid batteries, the main components of the positive and negative electrodes are lead sulfate, and the current flows from the positive electrode to the negative electrode.
● Graphene batteries: graphene conductive additives are added to the positive and negative electrode materials, graphene composite electrode materials are added to the positive electrode, and graphene functional layers are added to the conductive layers.
1.3 What does the information on the certificate represent?
● 6-DZF-20: 6 means there are 6 grids, each grid has a voltage of 2V, and the voltage connected in series is 12V, and 20 means the battery has a capacity of 20AH.
● D (electric), Z (power-assisted), F (valve-regulated maintenance-free battery).
● DZM: D (electric), Z (power-assisted vehicle), M (sealed maintenance-free battery).
● EVF: EV (battery vehicle), F (valve-regulated maintenance-free battery).
1.4 The difference between valve controlled and sealed
● Valve-regulated maintenance-free battery: no need to add water or acid for maintenance, the battery itself is a sealed structure, no acid leakage or acid mist, with a one-way safety exhaust valve, when the internal gas exceeds a certain value, the exhaust valve automatically opens to exhaust the gas
● Sealed maintenance-free lead-acid battery: the entire battery is fully enclosed (the battery's redox reaction is circulated inside the sealed shell), so the maintenance-free battery has no "harmful gas" overflow
2. Lithium Batteries
2.1 What is Lithium Batteries?
● Lithium batteries are a type of battery that uses lithium metal or lithium alloy as positive/negative electrode materials and uses non-aqueous electrolyte solutions. (Lithium salts and organic solvents)
2.2 Lithium Battery Classification
● Lithium batteries can be roughly divided into two categories: lithium metal batteries and lithium ion batteries. Lithium ion batteries are superior to lithium metal batteries in terms of safety, specific capacity, self-discharge rate and performance-price ratio.
● Due to its own high technological requirements, only companies in a few countries are producing this type of lithium metal battery.
2.3 Lithium Ion Battery
| Positive Electrode Materials | Nominal Voltage | Energy Density | Cycle Life | Cost | Security | Cycle Times | Normal Operating Temperature |
| Lithium Cobalt Oxide (LCO) | 3.7V | Medium | Low | High | Low | ≥500 300-500 |
Lithium iron phosphate: -20℃~65℃ Ternary lithium: -20℃~45℃Ternary lithium batteries are more efficient than lithium iron phosphate at low temperatures, but are not as resistant to high temperatures as lithium iron phosphate. However, this depends on the specific conditions of each battery factory. |
| Lithium Manganese Oxide (LMO) | 3.6V | Low | Medium | Low | Medium | ≥500 800-1000 |
|
| Lithium Nickel Oxide (LNO) | 3.6V | High | Low | High | Low | No data | |
| Lithium Iron Phosphate (LFP) | 3.2V | Medium | High | Low | High | 1200-1500 | |
| Nickel Cobalt Aluminum (NCA) | 3.6V | High | Medium | Medium | Low | ≥500 800-1200 |
|
| Nickel Cobalt Manganese (NCM) | 3.6V | High | High | Medium | Low | ≥1000 800-1200 |
● Negative electrode materials: Graphite is mostly used. In addition, lithium metal, lithium alloy, silicon-carbon negative electrode, oxide negative electrode materials, etc. can also be used for negative electrode
● By comparison, lithium iron phosphate is the most cost-effective positive electrode material.
2.4 Lithium-ion battery shape classification

Cylindrical lithium-ion battery

Prismatic Li-ion Battery

Button lithium ion battery

Special-shaped lithium-ion battery

Soft pack battery
● Common shapes used for electric vehicle batteries: cylindrical and soft-pack
● Cylindrical lithium battery:
● Advantages: mature technology, low cost, small single energy, easy to control, good heat dissipation
● Disadvantages: a large number of battery packs, relatively heavy weight, slightly lower energy density
● Soft-pack lithium battery:
● Advantages: superimposed manufacturing method, thinner, lighter, higher energy density, more variations when forming a battery pack
● Disadvantages: poor overall performance of the battery pack (consistency), not resistant to high temperatures, not easy to standardize, high cost
● Which shape is better for lithium batteries? In fact, there is no absolute answer, it mainly depends on demand
● If you want low cost and good overall performance: cylindrical lithium battery > soft-pack lithium battery
● If you want small size, light, high energy density: soft-pack lithium battery > cylindrical lithium battery
2.5 Lithium Battery Structure
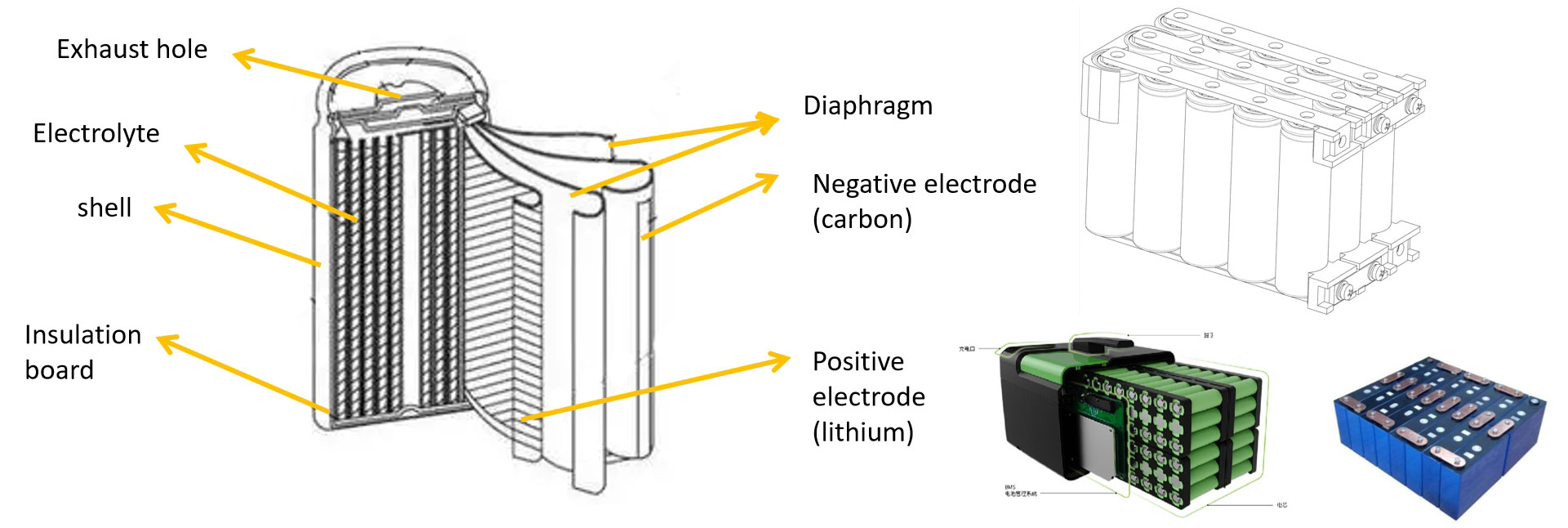
● 18650: 18mm indicates the diameter of the battery, 65mm indicates the height of the battery, 0 indicates a cylindrical shape, and so on
● Calculation of 12v20ah lithium battery: Assume that the nominal voltage of a 18650 battery is 3.7V (4.2v when fully charged) and the capacity is 2000ah (2ah)
● To get 12v, you need 3 18650 batteries (12/3.7≈3)
● To get 20ah, 20/2=10, you need 10 groups of batteries, each with 3 12V.
● 3 in series is 12V, 10 in parallel is 20ah, that is, 12v20ah (a total of 30 18650 cells are required)
● When discharging, the current flows from the negative electrode to the positive electrode
● When charging, the current flows from the positive electrode to the negative electrode
3. Comparison Between Lithium Battery, Lead-acid Battery and Graphene Battery
| Comparison | Lithium battery | Lead-acid battery | Graphene battery |
| Price | High | Low | Medium |
| Safety factor | Low | High | Relatively high |
| Volume and weight | Small size, light weight | Large size and heavy weight | Large volume, heavier than lead-acid battery |
| Battery life | High | Normal | Higher than lead-acid battery, lower than lithium battery |
| Lifespan | 4 years (ternary lithium: 800-1200 times lithium iron phosphate: 1200-1500 times) |
3 years (3-500 times) | 3 years (>500 times) |
| Portability | Flexible and easy to carry | Cannot be charged | Cannot be charged |
| Repair | Non-repairable | Repairable | Repairable |
● There is no absolute answer to which battery is better for electric vehicles. It mainly depends on the demand for batteries.
● In terms of battery life and life: lithium battery > graphene > lead acid.
● In terms of price and safety factor: lead acid > graphene > lithium battery.
● In terms of portability: lithium battery > lead acid = graphene.
4. Battery Related Certificates
● Lead-acid battery: If the lead-acid battery passes the vibration, pressure difference, and 55°C temperature tests, it can be exempted from ordinary cargo transportation. If it does not pass the three tests, it is classified as dangerous goods category 8 (corrosive substances)
● Common certificates include:
● Certification for Safe Transport of Chemical Goods (air/sea transport);
● MSDS (MATERIAL SAFETY DATA SHEET);
● Lithium battery: classified as Class 9 dangerous goods export
● Common certificates include: lithium batteries are commonly UN38.3, UN3480, UN3481 and UN3171, dangerous goods package certificate, freight transportation conditions appraisal report
● UN38.3 safety inspection report
● UN3480 lithium-ion battery pack
● UN3481 lithium-ion battery installed in equipment or lithium electronic battery and equipment packaged together (same dangerous goods cabinet)
● UN3171 battery-powered vehicle or battery-powered equipment (battery placed in the car, the same dangerous goods cabinet)
5. Battery Issues
● Lead-acid batteries are used for a long time, and the metal connections inside the battery are prone to breakage, causing short circuits and spontaneous combustion. Lithium batteries are over the service life, and the battery core is aging and leaking, which can easily cause short circuits and high temperatures.
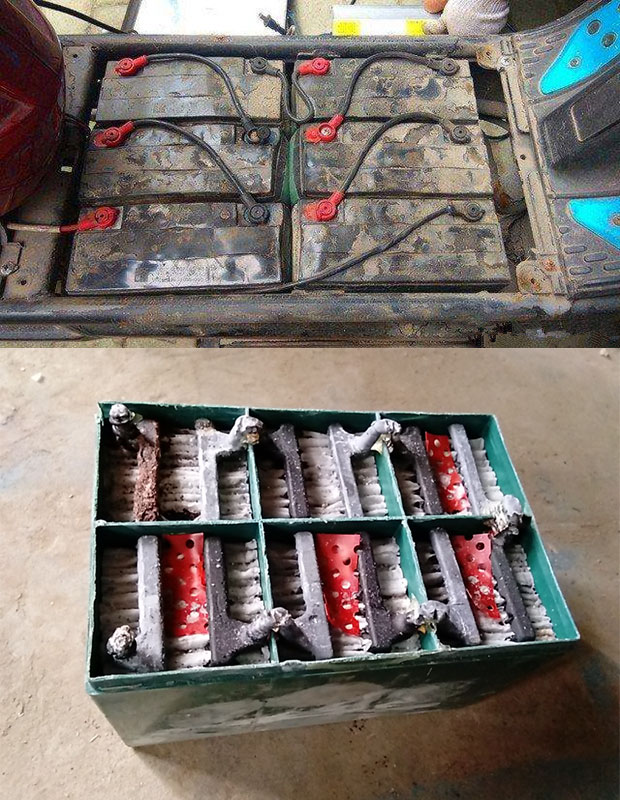

Lead-acid Batteries
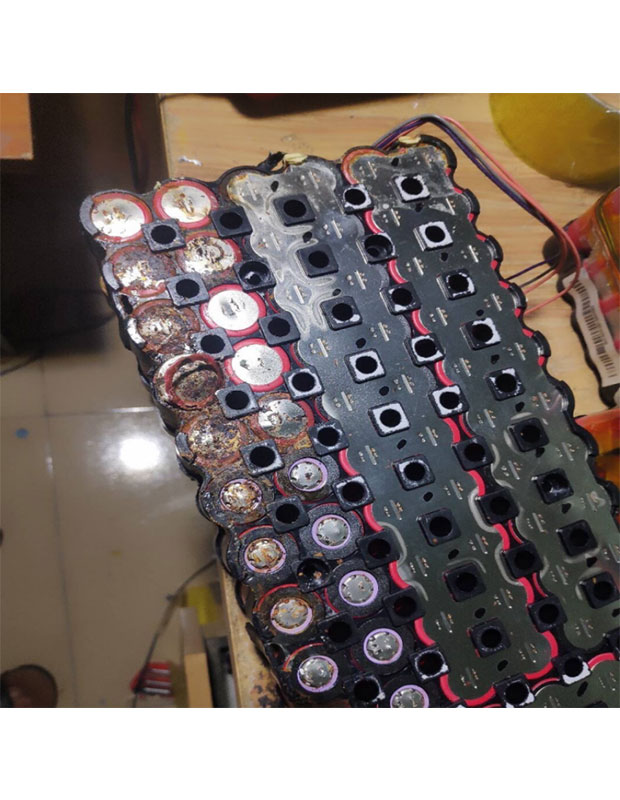

Lithium Battery
● Unauthorized modification: Users modify the battery circuit without authorization, which affects the safety performance of the vehicle's electrical circuit. Improper modification causes the vehicle circuit to be overloaded, overloaded, heated, and short-circuited.
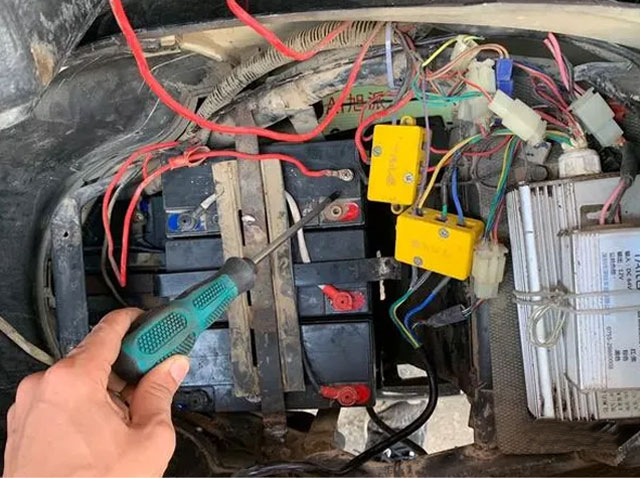

Lead-acid Batteries
Lithium Battery
● Charger failure. If the charger is left in the car for a long time and shakes, it is easy to cause the capacitors and resistors in the charger to loosen, which can easily lead to overcharging of the battery. Taking the wrong charger can also cause overcharging.

● Electric bicycles are exposed to the sun. In summer, the temperature is high and it is not suitable to park electric bicycles outside in the sun. The temperature inside the battery will continue to rise. If you charge the battery immediately after getting home from get off work, the temperature inside the battery will continue to rise. When it reaches the critical temperature, it is easy to spontaneously ignite.

● Electric motorcycles are easily soaked in water during heavy rain. Lithium batteries cannot be used after being soaked in water. Lead-acid battery electric vehicles need to be repaired in a repair shop after being soaked in water.
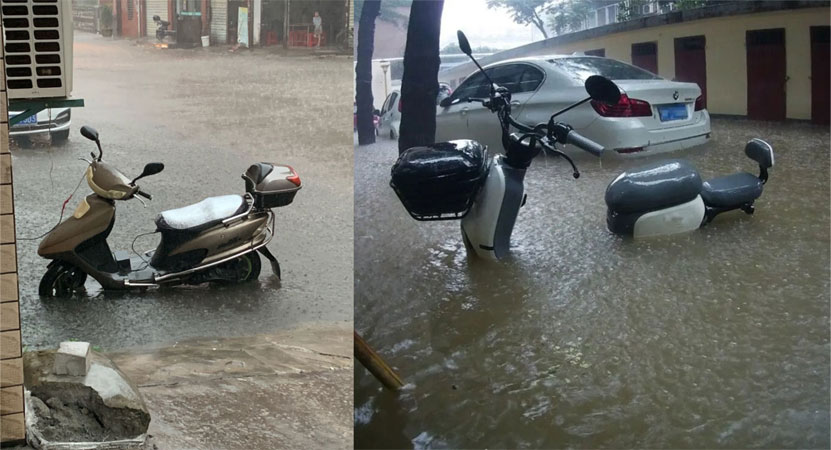

6. Daily Maintenance and Use of Batteries and Others
● Avoid overcharging and over-discharging of the battery
Overcharging: Generally, charging piles are used for charging in China. When fully charged, the power supply will be automatically disconnected. When charging with a charger, the power will be automatically disconnected when fully charged. In addition to ordinary chargers without full-charge power-off function, when fully charged, they will continue to charge with a small current, which will affect the life for a long time;
Over-discharging: It is generally recommended to charge the battery when there is 20% power left. Charging with low power for a long time will cause the battery to be under-voltage, and it may not be charged. It needs to be activated again, and it may not be activated.
● Avoid using it in high and low temperature conditions. High temperature will intensify the chemical reaction and generate a lot of heat. When the heat reaches a certain critical value, it will cause the battery to burn and explode.
● Avoid fast charging, which will cause changes in the internal structure and instability. At the same time, the battery will heat up and affect the battery life. According to the characteristics of different lithium batteries, for a 20A lithium manganese oxide battery, using a 5A charger and a 4A charger under the same conditions of use, using a 5A charger will reduce the cycle by about 100 times.
● If the electric vehicle is not used for a long time, try to charge it once a week or every 15 days. The lead-acid battery itself will consume about 0.5% of its own power every day. It will consume faster when installed on a new car.
Lithium batteries will also consume power. If the battery is not charged for a long time, it will be in a state of power loss and the battery may be unusable.
A brand new battery that has not been unpacked needs to be charged once for more than 100 days.
● If the battery has been used for a long time and has low efficiency, the lead-acid battery can be added with electrolyte or water by professionals to continue to be used for a period of time, but under normal circumstances, it is recommended to replace the new battery directly. The lithium battery has low efficiency and cannot be repaired. It is recommended to replace the new battery directly.
● Charging problem: The charger must use a matching model. 60V cannot charge 48V batteries, 60V lead-acid cannot charge 60V lithium batteries, and lead-acid chargers and lithium battery chargers cannot be used interchangeably.
If the charging time is longer than usual, it is recommended to unplug the charging cable and stop charging. Pay attention to whether the battery is deformed or damaged.
● Battery life = voltage × battery ampere × speed ÷ motor power This formula is not suitable for all models, especially high-power motor models. Combined with the usage data of most female users, the method is as follows:
48V lithium battery, 1A = 2.5km, 60V lithium battery, 1A = 3km, 72V lithium battery, 1A = 3.5km, lead-acid is about 10% less than lithium battery.
48V battery can run 2.5 kilometers per ampere (48V20A 20×2.5=50 kilometers)
60V battery can run 3 kilometers per ampere (60V20A 20×3=60 kilometers)
72V battery can run 3.5 kilometers per ampere (72V20A 20×3.5=70 kilometers)
● The capacity of the battery/the A of the charger is equal to the charging time, charging time = battery capacity/charger A number, for example 20A/4A = 5 hours, but because the charging efficiency will be slower after charging to 80% (pulse will reduce the current), so it is usually written as 5-6 hours or 6-7 hours (for insurance)


